Smart Grid Market Analysis Emphasizes Resilience Cybersecurity And DER Integration
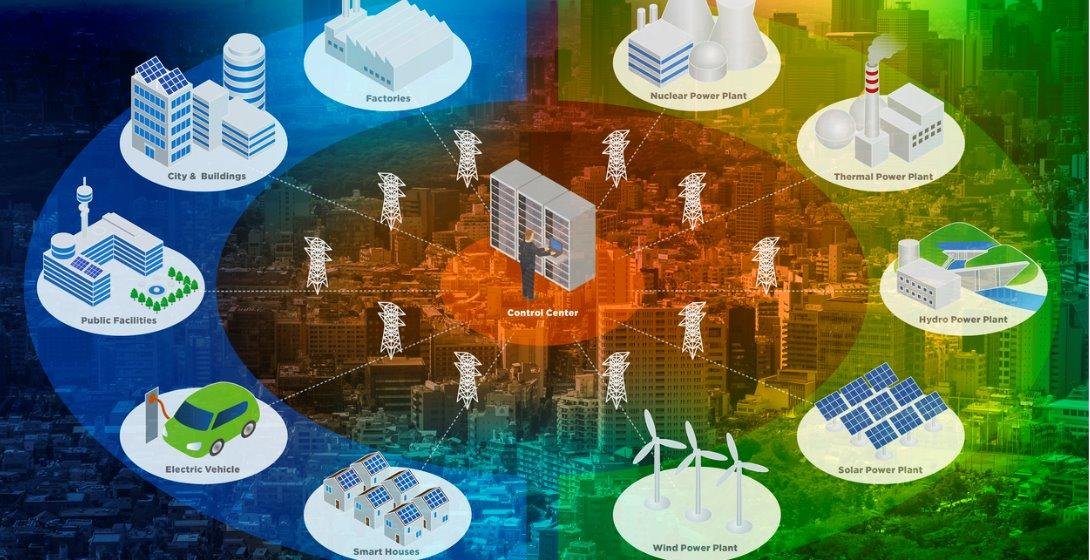

A detailed Smart Grid Market Analysis shows utilities investing to address aging infrastructure, reliability targets, and rising complexity from distributed energy resources. Smart grid spending is driven by the need to reduce outages, improve situational awareness, and integrate renewables and EV charging without destabilizing the grid. Market analysis highlights advanced metering infrastructure as a foundational investment, enabling interval data, outage detection, and customer programs such as time-of-use pricing. Distribution automation is another key area, with sensors and automated switches reducing restoration time through fault isolation and self-healing. Software platforms—SCADA, OMS, ADMS, DERMS—are central to orchestration and decision support. The analysis also notes that smart grid value depends on integration. Siloed deployments of meters or sensors deliver limited benefit unless connected to operations workflows and analytics. Therefore, utilities increasingly invest in interoperability, data platforms, and network models. The market is also influenced by regulatory mandates and modernization funding, which accelerate deployment in many regions.
Resilience is a dominant theme in market analysis. Extreme weather increases outage risk and accelerates investment in automation, monitoring, and microgrids. Utilities use smart grid systems to improve fault location, enhance crew dispatch, and provide accurate customer outage information. Grid modernization also supports wildfire mitigation through better monitoring and sectionalizing capabilities. Cybersecurity is equally emphasized. Digitization expands the attack surface, and critical infrastructure regulations require stronger protections. Market analysis highlights investments in secure communications, segmentation, identity controls, and continuous monitoring for operational technology networks. Utilities also implement supply chain risk management for connected devices and software. Workforce readiness is another constraint: operating modern platforms requires data, networking, and software skills. Many utilities rely on vendors and managed services to accelerate deployments and maintain systems. The analysis also points to customer engagement as a growing factor. Demand response and dynamic pricing programs require customer trust, clear benefits, and equitable design. Without participation, flexibility benefits are limited, especially as EV loads and distributed solar continue growing.
DER integration is a major driver and challenge. Distributed solar, batteries, and EV chargers introduce bidirectional power flows and localized congestion. Market analysis shows increasing demand for DERMS and advanced distribution management capabilities that coordinate these resources. Utilities also require better forecasting and visibility at the distribution edge, where legacy systems have limited sensors. EV charging management becomes a priority as electrification increases peak loads and transformer stress. Smart grid technologies enable managed charging programs and grid-interactive tariffs. The analysis notes that interoperability remains a critical issue because DER devices often come from many vendors. Standards-based control and clear data governance help reduce integration friction. Data management is another major theme; AMI and sensor networks generate massive data volumes, requiring scalable storage and analytics. AI and machine learning are increasingly used for load forecasting, outage prediction, and anomaly detection, but utilities demand validation and explainability due to operational risk. The market also faces long utility procurement cycles, making vendor stability and lifecycle support important selection criteria.
The analysis outlook suggests sustained investment as electrification and renewable integration continue. Utilities will increasingly treat smart grid programs as multi-year transformation initiatives, combining technology with operational redesign and cybersecurity governance. Phased rollouts—targeting high-outage feeders, critical substations, or EV-heavy neighborhoods—help demonstrate value and build internal capability. Market analysis recommends clear KPIs: SAIDI/SAIFI, loss reduction, voltage profile improvement, faster restoration, and reduced truck rolls. Integration strategy is crucial; utilities must connect OT platforms with enterprise systems while maintaining security boundaries. As flexibility markets and virtual power plants expand, utilities will coordinate third-party resources more actively, increasing platform requirements for consent management and secure control. The market will also see more edge intelligence and automation to support resilience during communications disruptions. Overall, smart grid market analysis indicates that modernization is no longer optional. It is required to deliver reliable, affordable power while managing distributed complexity, cybersecurity risk, and climate-driven resilience needs across modern electricity systems.
Top Trending Reports:
Mobile Collaboration Productivity And Innovation From Workplace Market
- Domain
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- Ссылки